At JuaTech Africa, our work begins where confusion usually ends. Technology should not feel like a secret language reserved for engineers or marketing departments. Tech Decoded exists to translate complex systems into precise, dependable knowledge that empowers everyday users, professionals, and enthusiasts alike. This RAM explainer is designed as a reference point—deep, rigorous, and accessible—so that anyone who reads it never looks at a spec sheet the same way again.
Why RAM Deserves to Be Decoded Properly
Random Access Memory—RAM—is one of the most frequently mentioned specifications in modern devices and among the least understood. It is often marketed as a symbol of power, longevity, or premium status, yet many users who buy devices with “more RAM” still encounter slowdowns, app reloads, and inconsistent performance.
The problem is not RAM itself. The problem is how RAM is explained.
RAM sits quietly beneath every interaction you have with a phone, tablet, or computer. It shapes how responsive a device feels, how reliably it multitasks, and how gracefully it handles pressure. Understanding RAM is not about chasing bigger numbers; it is about understanding how modern computing actually works.
This article approaches RAM from first principles, real-world behaviour, and system-level thinking—the JuaTech Africa way.
What RAM Is, from First Principles
RAM, or Random Access Memory, is a device’s short-term working memory. It is where data lives temporarily while the system is actively using it.
To understand why RAM exists, it helps to understand a fundamental limitation of computing: permanent storage is slow compared to the speed at which processors operate. Even the fastest modern storage cannot keep up with a processor if it were accessed directly for every operation. RAM acts as a high-speed buffer between storage and the processor.
A practical way to think about this is in terms of physical space. Storage is like a warehouse where everything you own is kept safely and permanently. RAM is like the desk where you spread out the items you are actively working on. You do not empty the warehouse every time you work, nor do you keep everything on the desk at all times. You move things back and forth as needed.
This temporary nature is what makes RAM fast. It does not concern itself with long-term organisation or durability. Its only job is to be immediately accessible.
Why RAM Is Temporary—and Why That Matters
RAM clears when a device powers off or restarts. This behaviour often confuses users, but it is essential to performance and stability.
Temporary memory allows systems to prioritise speed over permanence. It also allows the operating system to reorganise memory based on current needs constantly. Over time, applications change their behaviour, background tasks start and stop, and workloads shift. Clearing RAM resets this landscape, which is why a restart often makes a sluggish device feel fresh again.
RAM is not designed to “remember.” It is designed to respond.
What RAM Actually Does in Everyday Use
RAM’s role becomes clear when translated into daily interactions.
When an app is launched, essential components are moved into RAM so the processor can access them instantly. As you move between apps, available RAM decides whether they remain active in the background or are closed to make room for new tasks. At the same time, everyday functions such as notifications, music playback, and location updates continue running quietly in the background, coordinated by RAM so they do not disrupt what you are actively doing.
In practice, RAM governs continuity. A device with sufficient RAM feels calm under pressure. A device with limited RAM feels jumpy, reloads often, and breaks your flow.
Importantly, RAM does not make tasks faster in isolation. It prevents performance from collapsing when multiple tasks compete for attention.
RAM Capacity vs RAM Speed: Understanding the Difference Clearly
Two aspects define RAM: how much there is and how fast it operates.
RAM capacity, measured in Gigabytes, determines how many active processes a device can comfortably support at once. More capacity means more room for multitasking and fewer forced app closures.
RAM speed, defined by memory standards such as LPDDR4X, LPDDR5, or LPDDR5X, determines how quickly data can be accessed and moved. Faster RAM improves responsiveness under load and reduces power consumption during intensive tasks.
However, these two factors do not exist in isolation. A large amount of slow RAM can be undermined by inefficiency. A smaller amount of fast RAM can outperform it if managed intelligently. This is why JuaTech Africa consistently emphasises system balance over raw specifications.
The Role of the Operating System in RAM Management
RAM is not simply installed and left alone. The operating system actively manages it.
Modern operating systems constantly decide which apps remain active, which are paused, and which are closed when memory pressure increases. They prioritise frequently used applications, background services, and system stability.
This is why two devices with identical RAM can behave very differently. One may feel smooth and consistent, while the other feels aggressive and unreliable. The difference lies in the memory management philosophy, not in the amount of memory.
Understanding RAM without understanding software is incomplete.
Virtual RAM and Memory Expansion Explained Honestly
Virtual RAM, sometimes marketed as RAM expansion, uses a portion of storage as overflow memory when physical RAM is under pressure.
This technique can reduce the number of extreme app closures on devices with limited RAM, but it has strict limitations. Storage, no matter how fast, is significantly slower than physical RAM. Virtual RAM cannot replace real memory, nor can it deliver the same responsiveness.
Its value lies in stability, not performance. When marketed honestly, it is a supporting mechanism. When marketed as a performance upgrade, it becomes misleading.
RAM and Battery Life: A Subtle Relationship
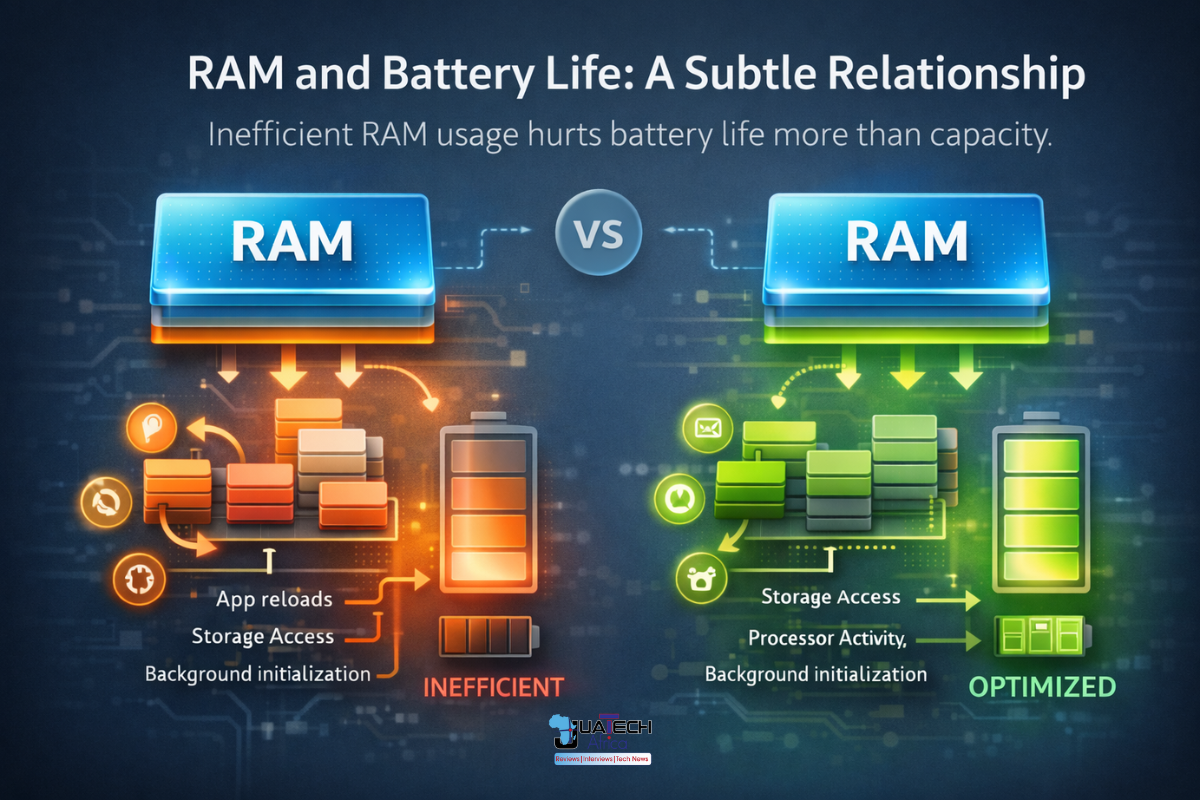
It is often assumed that more RAM drains more battery. In reality, inefficient RAM usage is far more damaging to battery life than capacity itself.
When RAM is insufficient, apps reload frequently. Each reload triggers processor activity, storage access, and background initialisation—all of which consume power. Adequate RAM can reduce this churn, leading to smoother operation and more stable battery behaviour.
Efficiency, once again, matters more than raw numbers.
RAM in the Context of the Whole System
RAM does not exist alone. Its effectiveness depends on the processor, storage speed, thermal design, and software optimisation. A balanced system with moderate RAM can outperform a poorly integrated system with excessive RAM.
This is why evaluating RAM in isolation leads to poor decisions. It must always be considered as part of a wider architecture.
Frequently Asked Questions: RAM Fully Explained
- What does RAM actually do in a phone?
RAM temporarily holds the data and instructions that the processor needs immediately, enabling fast app launches, smooth multitasking, and stable background activity. - Does more RAM make a phone faster?
More RAM helps a phone remain responsive under load, but it does not increase raw processing speed. - Why do apps reload when I switch back to them?
App reloads occur when the system frees RAM to accommodate other processes, often due to limited memory capacity. - Is unused RAM wasted?
No. Modern systems intentionally keep RAM occupied to improve responsiveness through caching. - How much RAM is enough for most users?
For most users, 6–8GB offers an excellent balance between performance and longevity. - Why do some phones feel smooth with less RAM?
Efficient software and disciplined memory management can compensate for a smaller RAM capacity. - What is LPDDR RAM?
LPDDR is a low-power memory designed for mobile devices that balances speed and energy efficiency. - Is LPDDR5 better than LPDDR4X?
Yes, LPDDR5 offers higher bandwidth and better power efficiency, especially under heavy workloads. - Does RAM affect gaming performance?
RAM supports gaming stability and asset loading, but the processor and GPU play larger roles. - What is virtual RAM?
Virtual RAM uses storage as temporary memory overflow when physical RAM is under pressure. - Is virtual RAM a replacement for physical RAM?
No. It is slower and should be seen as a support mechanism, not a substitute. - Can RAM wear out over time?
No. RAM does not degrade through regular use in consumer devices. - Why does restarting a device improve performance?
Restarting clears RAM, resets processes, and removes accumulated inefficiencies. - Does RAM affect battery life?
Indirectly. Adequate RAM can reduce reloads and processor strain, improving efficiency. - Is 12GB or 16GB RAM future-proof?
It can help with longevity, but only if the processor and software support remain strong. - Why do budget phones struggle even with decent RAM?
Weak processors and slow storage can bottleneck performance before RAM becomes useful. - Does closing apps manually save RAM?
Often no. Modern systems manage memory more efficiently than manual intervention. - Is RAM more important than storage speed?
Both matter. Slow storage can undermine RAM by delaying data movement. - How does multitasking really depend on RAM?
Multitasking relies on RAM to keep multiple apps active without interruption. - What is the biggest misconception about RAM?
That bigger numbers automatically equal a better experience. Balance and optimisation matter more.
Final Perspective: Why This Explainer Exists
RAM is not a badge of superiority. It is a structural component of modern computing that quietly shapes how technology feels day after day.
At JuaTech Africa, Tech Decoded is built on the belief that understanding precedes empowerment. When users understand RAM correctly, they stop being driven by marketing noise and start making informed, confident decisions.
This article is designed to stand as a reference—something readers return to, quote, and trust. That is how an intelligence hub is built: with patience, depth, and clarity.
Tech Decoded continues.